E-commerce Personalization: Revolutionizing Online Shopping
Dec 17, 2023 in E-Commerce Solutions, Online Marketing by Hami Uğur Aksakal
E-commerce personalization has become a cornerstone of customer-centric marketing strategies. With 80% of customers more likely to purchase when brands offer personalized experiences and 70% of consumers spending more with companies that provide seamless, tailored experiences, the importance of personalization in e-commerce is undeniable.
From basic personalization techniques like customer names and location-based customization to advanced AI-driven strategies, personalization encompasses a vast spectrum of approaches, each designed to elevate the customer experience. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of e-commerce personalization, exploring its three levels—basic, intermediate, and advanced—and their impact on enhancing consumer shopping experiences.
- What is E-commerce Personalization?
- What is Basic Personalization?
- What is Intermediate Personalization?
- What is Advanced Personalization?
- Why is Personalization Important in E-commerce?
- How Does E-commerce Personalization Enhance the Shopping Experience for Consumers?
- 1. Relevancy in Product Offerings
- 2. Customized Content
- 3. Individualized Discounts and Promotions
- 4. Personalized Search Functionality
- 5. Real-Time Assistance
- How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with E-commerce Businesses?
- Displaying Products Relevant to The Customer's Interests and Past Purchases
- Tailoring the Product Search Experience
- Chatbots and Customer Support
- Personalizing Pricing and Promotions
- Personalizing the Shopping Cart Experience
- Personalizing the Checkout Process
- Personalizing Post-Purchase Communications
- Customized Emails and Marketing Messages
- Social Media Personalization
- Mobile App Personalization
- What are The Personalization Ways in Different Business Models?
- Personalization in B2C
- Personalization in B2B
- What is the Difference Between B2C and B2B Personalization?
- How to Tailor Personalization Strategies to Different Business Types
- How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with Subscription-Based Models?
- 1. Tailored Product Selection
- 2. Personalized Communication
- 3. Dynamic Pricing and Offers
- 4. Predictive Analytics
- 5. Enhanced Onboarding Experience
- 6. Feedback and Reviews
- 7. Seasonal or Event-Based Customization
- 8. Cross-Selling and Upselling
- How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with Service-Based Businesses?
- 1. Tailored Service Recommendations
- 2. Customized Communication
- 3. Dynamic Content Display
- 4. Personalized Booking Experience
- 5. Feedback-Driven Service Improvement
- How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with Local Businesses?
- 1. Geo-Targeted Promotions
- 2. Local Event Participation
- 3. Community-Based Personalization
- 4. Local Delivery Options
- 5. Customized Loyalty Programs
- 6. Local Partnerships and Collaborations
- 7. Social Media Engagement
- 8. Localized SEO and Content
- What are The Benefits of Implementing E-Commerce Personalization Strategies?
- How to Develop a Personalization Strategy
- 1. Data Analysis
- 2. Segmentation and Grouping
- 3. Consumer Profiling
- 4. Using AI and Algorithms for Recommendations
- 5. Dynamism
- 6. Ads Campaigns
- 7. Cross-Channel Personalization
- 8. Optimization
- 9. Privacy and Transparency
- 10. Be Future-Oriented
- How is The Technical Side of E-commerce Personalization?
- What is The Role of AI and Machine Learning in E-Commerce Personalization?
- Analysis
- Content Generation
- Privacy and Evolution
- What Are The Best Practices for Ethical and Effective E-Commerce Personalization?
- Transparency
- Security
- Improvement
- What is The Future of E-Commerce Personalization?
- Blockchain as Security
- Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
- Predictive Analysis
- Sound in E-Commerce
- Sustainability
- What are The Differences Between Personalization and Customization in E-Commerce?
- Final Say
What is E-commerce Personalization?
E-commerce personalization is individualizing each online experience to meet customer preferences, behaviors, and needs. It uses technology and data research to deliver personalized content and offer unique recommendations for each customer. These recommendations and personalization are derived from the consumers’ past interactions. Some of these are their previous purchases, browsing behaviors, geographic locations, and personal information.
There are 3 steps of personalization in e-commerce:
- Basic Personalization
- Intermediate Personalization
- Advanced Personalization

What is Basic Personalization?
Basic personalization in e-commerce refers to the fundamental techniques used to tailor an online shopping experience to individual customers based on their general behaviors and characteristics. It typically includes:
- Using Customer Names: Personalizing emails and other communications by addressing customers by name.
- Location-Based Customization: Tailoring the shopping experience based on the customer's geographic location, such as showing local currency, shipping options, and regional promotions.
- Displaying Recently Viewed or Purchased Items: Showcasing products that customers have recently viewed or bought on the website.
- Basic Product Recommendations: Offering product suggestions based on broad customer segments or popular trends rather than highly individualized customer data.
- Segmentation-Based Email Marketing: Email campaigns are segmented based on essential criteria like demographics (age, gender) or past purchase behavior.
- Seasonal or Event-Related Offers: Providing promotions and deals relevant to upcoming holidays, seasons, or events that cater to a broad audience.
These basic personalization strategies are relatively simple and can significantly enhance the customer experience by making it seem more tailored and engaging.
What is Intermediate Personalization?
Intermediate personalization goes beyond basic techniques, incorporating more detailed customer data to create a more tailored experience. It typically involves:
- Behavioral-Based Recommendations: Suggesting products based on a customer's browsing history, past purchases, and in-session behavior on the website.
- Segmentation Using More Data Points: Creating customer segments based on a wider range of data, such as browsing habits, purchase frequency, and customer lifecycle stage.
- Personalized Email Campaigns: Crafting email content that resonates with specific segments, like cart abandonment emails or product recommendations based on past purchases.
- Dynamic Content on Websites: Displaying content that changes based on the user's profile or in-session actions, such as showing different homepage banners to new visitors versus returning customers.
- Retargeting Across Channels: Implementing retargeting campaigns that follow users across different platforms or devices with tailored advertisements based on their interactions on the e-commerce site.
- Personalized Discounts and Offers: Providing special deals or promotions based on a customer's purchase history or engagement level.
What is Advanced Personalization?
Advanced personalization represents the cutting edge of customization in e-commerce, utilizing sophisticated algorithms, AI, and machine learning to deliver highly individualized customer experiences. This includes:
- AI-Driven Product Recommendations: Using artificial intelligence to analyze vast amounts of data, predicting and suggesting products that a specific customer is likely to be interested in.
- Predictive Personalization: Anticipating a customer’s needs and preferences before they explicitly express them, based on predictive analytics.
- Individualized Customer Journeys: Creating unique shopping experiences for each customer based on their data profile, including browsing patterns, social media interactions, and purchase history.
- Real-Time Personalization: Dynamically changing website content and recommendations in real-time as a customer interacts with the site.
- Hyper-Segmentation: Utilizing micro-segmentation to create extremely specific customer groups based on nuanced behaviors, preferences, and interactions.
- Personalized Omnichannel Experiences: Integrating personalization across all channels, including online, mobile, and in-store, to provide a seamless and consistent experience.
- Voice and Visual Search Personalization: Tailoring search results and recommendations based on voice and image searches, leveraging natural language processing and image recognition technologies.
Advanced personalization strategies require significant technological infrastructure and data science capabilities but can lead to substantially improved customer experiences, higher engagement, and increased sales.
Why is Personalization Important in E-commerce?
Personalization in e-commerce is crucial because commerce personalization stems from its ability to provide a better consumer experience. It's a strategic imperative that can significantly impact customer experience, sales, loyalty, and business growth.
How Does E-commerce Personalization Enhance the Shopping Experience for Consumers?
E-commerce personalization is a key strategy for bridging the gap between brands and customers. It's not just about selling products but crafting a shopping journey that converts casual browsers into loyal customers. Personalization plays a crucial role in enhancing the customer's shopping experience in 5 ways:
1. Relevancy in Product Offerings
Relevancy is fundamental in e-commerce personalization. By analyzing customer data, including browsing and purchase history, hobbies, and preferences, brands can present products that align closely with the customer's interests. This tailored approach helps customers discover products they might not have found through generic browsing, significantly enhancing the likelihood of a purchase.
2. Customized Content
Beyond suggesting relevant products, personalization extends to the content customers encounter. This includes personalized newsletters, blog posts, and product descriptions, each tailored to the customer’s interests and previous interactions with the brand. This strategy goes beyond mere promotion, fostering a deeper connection between the customer and the brand.
3. Individualized Discounts and Promotions
One of the most effective ways to make customers feel valued is through individualized discounts and promotions. By tailoring these offers to customers based on their shopping habits and history, brands can create a sense of exclusivity and appreciation, fostering customer loyalty.
4. Personalized Search Functionality
The search bar is often the first point of interaction in an online shopping experience. Enhancing it with personalized autocomplete suggestions, filters, and recalling previous searches can significantly streamline the shopping process. This level of personalization in the search experience helps customers quickly find what they're looking for, improving their overall experience.
5. Real-Time Assistance
Navigating an extensive online catalog can be daunting for consumers. Providing real-time help through pop-ups or chatbots can guide customers during their shopping journey. This approach helps find the right products and adds a personal touch, making the shopping experience more engaging and less isolating.
E-commerce personalization is about more than increasing sales; it’s about creating an enriched, engaging shopping experience that resonates with consumers personally. By implementing these strategies, brands can significantly enhance the shopping experience, increasing customer satisfaction, loyalty, and, ultimately, brand success.

How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with E-commerce Businesses?
E-commerce personalization can be used in various ways to improve the customer experience and increase sales for e-commerce businesses. Here are some specific examples of how e-commerce personalization can be used:
Displaying Products Relevant to The Customer's Interests and Past Purchases
This can be done by using machine learning to analyze customer data and identify patterns in their behavior. This information can be used to personalize product recommendations, display relevant products on the homepage and product pages, and send targeted email campaigns.
Tailoring the Product Search Experience
This can be done using natural language processing to understand the customer's search intent. For example, if a customer searches for "black dress," the e-commerce platform could suggest different styles of black dresses based on the customer's past purchases and browsing history.
Chatbots and Customer Support
Implementing AI-driven chatbots that provide personalized assistance based on customer history and preferences can improve customer service and support.
Personalizing Pricing and Promotions
This can be done by using dynamic pricing algorithms to adjust prices based on the customer's location, purchase history, and browsing behavior. For example, an e-commerce platform could offer a discount on a product to a customer who has been browsing it for several days.
Personalizing the Shopping Cart Experience
This can be done by recommending complementary products to the customer's cart, offering discounts on abandoned carts, and sending reminders about items in the cart.
Personalizing the Checkout Process
This can be done by remembering the customer's shipping and billing information, suggesting pre-filled address fields, and offering personalized payment options.
Personalizing Post-Purchase Communications
This can be done by sending personalized thank-you emails, recommending similar products to the customer's purchase, and providing customer support based on the customer's past interactions.
Customized Emails and Marketing Messages
Sending personalized emails based on the customer's previous interactions, such as cart abandonment reminders or suggestions for products similar to those they've shown interest in, can significantly improve conversion rates.
Social Media Personalization
Using social media data to create personalized ad campaigns or content can attract potential customers and enhance the overall brand experience.
Mobile App Personalization
For businesses with mobile applications, personalizing the app experience based on user preferences and usage patterns can increase engagement and sales through the app.
What are The Personalization Ways in Different Business Models?
You can implement personalization techniques mainly in B2C (Business-to-Consumer) and B2B (Business-to-Business).
Personalization in B2C
Personalization in B2C aims to build bridges between the brand and the consumer by creating personal recommendations and content. In B2C environments like e-commerce, brands use personalized algorithms to provide the best precise suggestions based on their consumers’ browsing history and purchase habits. This, in turn, results in a perfect e-commerce personalization.
B2C personalization aims at shorter sales cycles. Such an example shows helping pop-ups whenever the consumer feels indecisive to make them buy the product they are unsure of. So, B2C personalization aims at immediate purchasing decisions while offering personalized promotions and recommendations.
Personalization in B2B
Personalization in B2B refers to tailoring offerings and experiences to the specific needs of businesses or organizations rather than individual consumers. One of the ways to achieve this for B2B personalization is through creating relationships.
With these built relationships, B2B personalization aims to create more relevant and accessible business transitions throughout the B2B environment. 3 key aspects of B2B personalization are Post-Sale Personalization, Cross-Departmental Engagement, and Relationship Building.
- Post-sale personalization is the idea of continuous support even after the sale is complete to ensure the relationship between the two businesses persists.
- Since B2B transactions require multiple stakeholders within a business, including the representatives of departments such as IT and finance, the resonance between these is a must. This is why Cross-Departmental Engagement is essential in ensuring that every system cog is working harmoniously.
- The primary aspect of B2B personalization is to create strong, long-term relationships across and within businesses. To achieve this, understanding the roles and responsibilities of the decision-makers and other components of the business is vital.
What is the Difference Between B2C and B2B Personalization?
The key differences between B2C (Business-to-Consumer) and B2B (Business-to-Business) personalization in e-commerce revolve around their target audiences, decision-making processes, content strategies, and data utilization techniques. Both approaches aim to tailor the customer experience, but they do so in ways that align with the distinct characteristics of their respective markets.
1. Target Audience
B2C Personalization: Focuses on individual consumers, often emphasizing emotional and impulsive buying decisions.
B2B Personalization: Targets other businesses, considering organizational needs, roles of various stakeholders, and overarching business objectives.
2. Decision-Making Process
B2C: Characterized by quicker, individual-based decisions driven by personal preferences, desires, or immediate needs.
B2B: Involves a longer, more rational decision-making process with multiple stakeholders, emphasizing the efficiency, ROI, and value offered to the business.
3. Content and Messaging
B2C: Content is emotionally appealing, focusing on individual interests, lifestyles, and consumer behaviors to establish a connection with the brand.
B2B: Centers around value-based content that addresses specific business challenges and goals, providing solutions and demonstrating ROI.
4. Data Utilization
B2C: Relies on consumer data such as browsing behavior, purchase history, and social media interactions to offer tailored recommendations and personalized marketing.
B2B: Utilizes data like industry type, company size, user roles, purchasing patterns, and engagement with educational content to create targeted outreach and content.
Examples
B2C: Includes personalized product recommendations, targeted email campaigns based on individual purchase history, and personalized discounts.
B2B: Features customized landing pages for different industries, personalized email campaigns addressing business challenges, and tailored educational content like whitepapers or webinars.
In essence, B2C personalization is about aligning with the emotional and individual aspects of consumer behavior, while B2B personalization is about understanding and addressing the specific needs and objectives of businesses and their decision-makers. Both require a nuanced approach to engage their respective audiences effectively.
How to Tailor Personalization Strategies to Different Business Types
Tailoring personalization strategies to various business types requires a rigorous understanding of the unique characteristics of these businesses. Here are the main steps to help you tailor personalization strategies for subscription-based, service-based, local and e-commerce businesses:
How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with Subscription-Based Models?
E-commerce personalization in subscription-based models can significantly enhance the customer experience, increase retention rates, and drive revenue growth. By tailoring the subscription experience to individual preferences and behaviors, businesses can create more value for their customers and foster long-term loyalty. Here are several ways to use personalization in subscription-based e-commerce models:
1. Tailored Product Selection
- Curated Experiences: Offer personalized product selections based on customer preferences, purchase history, and engagement. For instance, a beauty subscription box could include specific products based on the customer's skin type or style preferences.
- Customizable Subscriptions: Allow subscribers to personalize their boxes or services each cycle. This could involve selecting from a range of products, adjusting quantities, or choosing themes.
2. Personalized Communication
- Targeted Email Campaigns: Send personalized emails based on the subscriber's journey stage, past interactions, and preferences. This could include welcome emails, renewal reminders, and tailored content like tips or articles related to their interests.
- Engagement Through Social Media: Use data to understand subscriber interests and engage them on social media with relevant content, polls, or community discussions.
3. Dynamic Pricing and Offers
- Customized Pricing Plans: Offer pricing plans that align with usage patterns or customer segments. For example, a discounted annual subscription for loyal customers or tiered pricing based on usage levels.
- Special Promotions: Implement promotions or additional benefits for high-value customers, like exclusive access to new products or additional perks for long-term subscribers.
4. Predictive Analytics
- Anticipate Needs: Use predictive analytics to anticipate subscriber needs and preferences. For example, a meal subscription service might suggest new recipes based on dietary preferences and past meal ratings.
- Churn Prediction: Identify subscribers who may be at risk of canceling their subscriptions and proactively offer personalized incentives to retain them.
5. Enhanced Onboarding Experience
- Custom Onboarding: Create a personalized onboarding process that helps new subscribers understand and maximize the value of their subscription based on their specific interests and goals.
6. Feedback and Reviews
- Collect and Utilize Feedback: Regularly gather feedback from subscribers to improve the personalization of the products and services offered continuously. Utilize this feedback to refine product selections and user experiences.
7. Seasonal or Event-Based Customization
- Thematic Adjustments: Customize subscriptions based on seasons, holidays, or special events, offering relevant products or content that aligns with the time of year or special occasions.
8. Cross-Selling and Upselling
- Relevant Recommendations: Offer additional products or upgraded subscription options that complement the subscriber’s current preferences and purchase history.
Incorporating these personalization strategies in subscription-based e-commerce models can create a more engaging and satisfying customer experience, encouraging longer subscription lifetimes and deeper customer relationships.
How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with Service-Based Businesses?
Service-based businesses thrive on understanding and catering to individual client needs. By leveraging e-commerce personalization, these businesses can not only enhance their service offerings but also forge stronger, more meaningful relationships with their clients, ensuring a unique and satisfying customer journey at every touchpoint.
1. Tailored Service Recommendations
- Analyze customer interactions, preferences, and past services to recommend personalized services.
- For example, a digital marketing agency could suggest specific services like SEO or social media marketing based on a client's website performance or business type.
2. Customized Communication
- Send personalized emails or messages with service updates, tips, or advice relevant to the customer's business or needs.
- Implement chatbots on the website for personalized interaction, guiding customers to services that match their queries.
3. Dynamic Content Display
- Customize the website's content based on the visitor’s profile or past interactions, showcasing relevant services or case studies.
4. Personalized Booking Experience
- Offer a tailored booking interface where clients can see their frequently availed services or special offers based on their service history.
5. Feedback-Driven Service Improvement
- Collect and analyze customer feedback to personalize and improve service offerings.
E-commerce personalization transforms the way service-based businesses interact with their clients. By tailoring services and communications to individual preferences and needs, these businesses can significantly improve client satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term engagement, paving the way for sustained growth and success.
How can E-commerce Personalization be Used with Local Businesses?
Local businesses stand at the heart of community engagement, and through e-commerce personalization, they can deepen their connection with the local customer base. Personalization allows these businesses to tailor their online presence to reflect local tastes, trends, and community values, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
1. Geo-Targeted Promotions
- Use location data to provide personalized offers, discounts, or promotions relevant to the local area or community events.
2. Local Event Participation
- Personalize marketing efforts by integrating local events, festivals, or holidays into the online shopping experience.
3. Community-Based Personalization
- Tailor product recommendations or content based on popular trends or needs within the local community.
4. Local Delivery Options
- Provide personalized delivery options like same-day delivery or local pickup for customers in the vicinity.
5. Customized Loyalty Programs
- Develop loyalty programs that cater to local customers with rewards that resonate with the local community's preferences.
6. Local Partnerships and Collaborations
- Collaborate with other businesses for cross-promotion, offering personalized deals that benefit the local business ecosystem.
7. Social Media Engagement
- Use social media platforms to engage with the local community, sharing personalized content that reflects local interests and activities.
8. Localized SEO and Content
- Optimize the website and content for local SEO, ensuring the business appears in local search results.
The power of e-commerce personalization for local businesses lies in its ability to resonate with the community's unique preferences and needs. By integrating local flavors into their online strategies, these businesses strengthen customer loyalty and position themselves as integral and responsive members of the local ecosystem.
What are The Benefits of Implementing E-Commerce Personalization Strategies?
By implementing e-commerce personalization strategies, businesses can achieve a number of benefits, including:
- Increased customer satisfaction: Personalized experiences help customers feel valued and understood, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved conversion rates: By recommending relevant products and providing tailored messaging, e-commerce businesses increase customers' likelihood of purchasing.
- Higher average order value: Personalized recommendations help customers discover new products they may not have considered, leading to higher average order values.
- Increased brand loyalty: Personalization helps build customer relationships, leading to increased brand loyalty and repeat business.
In addition to these benefits, e-commerce personalization can also help businesses to:
- Target marketing campaigns more effectively: By understanding customer preferences and behaviors, businesses create more targeted marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with customers.
- Reduce customer churn: Personalized experiences help to keep customers engaged and prevent them from churning to competitors.
- Gain a competitive advantage: By investing in e-commerce personalization, businesses differentiate themselves from competitors and gain a competitive advantage.
E-commerce personalization is a powerful tool that can be used to improve the customer experience, increase sales, and achieve various other business goals. By implementing e-commerce personalization strategies, businesses can create a more personalized and engaging shopping experience for their customers, increasing customer satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue.
How to Develop a Personalization Strategy
An excellent E-commerce personalization strategy refers to a specific brand approach. Starting from their products and services, brands should prioritize personalizing them based on their consumers' preferences, behaviors, and needs.
When creating E-commerce personalization strategies, you can follow 10 steps below to ensure versatility and directness, laying the foundation for success.
- Data Analysis
- Segmentation and Grouping
- Consumer Profiling
- Using AI and Algorithms for Recommendations
- Dynamism
- E-mail Campaigns
- Cross-Channel Personalization
- Optimization
- Privacy and Transparency
- Be Future-Oriented
1. Data Analysis
The first thing to do before creating a strategy is to gather all consumer data information. Since it is the most important part, giving the utmost attention to it is necessary and an obligation. Gathering data from the consumers’ browsing histories, purchase behaviors, preferences, and demographic information is a must. However, it must be precise and accurate. To ensure no problems, utilize data analytics tools to gain insight about your consumers.
2. Segmentation and Grouping
Once you have analyzed your consumer base, divide it into segments. However, you should divide them based on common characteristics, behaviors, and preferences. This way, you can tailor your products and services better since the scope of personalization is narrowed.
3. Consumer Profiling
Create detailed user profiles corresponding to each group. While creating these profiles, include information about their past purchases, which products they have viewed, their search histories, and any other relevant information. Then, use these profiles as stemming points to personalize the shopping experience according to your consumer base.
4. Using AI and Algorithms for Recommendations
Use AI, such as recommendation engines, to suggest new products based on what the consumers have already purchased. Accurate suggestions will lead consumers to think valued and unique since the website they browse already knows their tastes. Also, opt for algorithms that will provide consumers with accurate and relevant product recommendations via email or message.
5. Dynamism
Dynamism is one of the most critical steps to creating an excellent strategy for e-commerce personalization. Since no definite content attracts all the consumers, you need to use different types of content. For example, provide content based on location. You can do this by creating unique product descriptions for different cultures and different languages. This way, your e-commerce personalization strategy will aim at more potential consumers.
6. Ads Campaigns
Providing a personalized experience involves the website. You can tailor personalized e-mail or SMS campaigns that include exclusive offers such as discounts. This way, even if the consumer is not actively searching for a service or a product, you can still maintain the connection. This way, consumers will feel like they are part of a constant relationship.
7. Cross-Channel Personalization
E-commerce doesn’t include only one specific technological device, such as personal computers, Macs, iPads, or tablets. Make sure you have full personalization across all the platforms to reach the maximum amount of consumers.
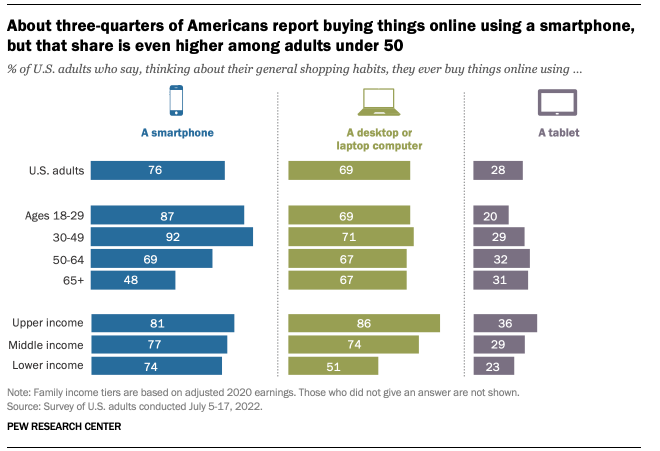
Losing the cross-channel personalization aspect is a vital problem for brands. For example, according to pewresearch.org, a Washington-based research center, 9 out of 10 Americans use their smartphones when buying things. So, creating a mobile-friendly website and making necessary personalization aspects for smartphone users will boost your revenue.
8. Optimization
Since cross-channel personalization is necessary to ensure you have the right tools to compete in this vast world of e-commerce, optimization is also necessary. Ensure that all your platforms are working fine by continuous testing. Also, try to develop new personalization options across and in platforms. Use A/B testing to assess the impact of these changes and adjust your strategy accordingly.
9. Privacy and Transparency
Always prioritize your consumers' privacy and be transparent about what data you are gathering and using to personalize their experiences better. One of the best ways to show your sincerity to your consumers is using explicit consent.
10. Be Future-Oriented
Develop a strategy that can scale as the consumer base grows to minimize future problems and errors. Upgrade your infrastructure and systems to a point that can handle increased data volume and advanced personalization options. Losing the option to move forward alongside technological advancements, you can miss out on significant chances and, thus, lose your grasp on your consumer database.
How is The Technical Side of E-commerce Personalization?
The main functions of technology in e-commerce personalization stem from its usage of AI and machine learning. They are used to analyze and leverage data to provide consumers with the best possible personalization options.
What is The Role of AI and Machine Learning in E-Commerce Personalization?
These two major technologies allow firms to analyze vast amounts of data and provide you with eligible strategies for your consumers. Here is a general overview of their 3 roles and how they function.
Analysis
- Machine learning algorithms analyze the consumers’ behavior patterns, such as their browsing histories, and provide the best possible personalization options.
- By looking through your consumers' data, these algorithms create a pattern, thus minimizing personalization errors. Thanks to this, they will also anticipate user needs and forecast future trends.
Content Generation
- These AIs can dynamically adjust the website according to their analysis and create relevant product listings and banners in real-time.
- Also, machine learning enables more advanced and precise consumer-categorization. This, in turn, results in more relevant e-commerce personalization for your consumers.
Privacy and Evolution
- Advanced machine learning can authenticate fraudulent activities and detect anomalies in user behaviors. Thus, they are vital components in protecting the safety of your consumers’ privacy.
- Machine learning models always strive to enhance themselves by updating newer versions. This way, you will be able to keep up with the ongoing trends and anticipate future ones.
What Are The Best Practices for Ethical and Effective E-Commerce Personalization?
E-commerce personalization can enhance user experience; however, it must be done respectfully to maintain the trust between the brand and the consumer. In the end, this trust is one of the most impactful forces that leads to higher sales numbers. To build and maintain this trust, here are the best practices for ethical and effective e-commerce personalization:
Transparency
Communicate with your consumers what type of data will be used for personalization clearly.
Security
Pay utmost attention to data security and implement strict protocols to protect user data from breaches and unauthorized access from third parties. Also, always configure and update your security base to avoid potential threats.
Improvement
Gather feedback from your consumers about their time on the brand’s website and how personalization affected their experiences. Then, use these data to improve on the personalization algorithm and refine the experience even more.
What is The Future of E-Commerce Personalization?
The future of e-commerce personalization is expected to be shaped by technological advancements, changing consumer expectations, and rapid adoption of these changes. Here are some of the ongoing and to-be-realized trends in the world of e-commerce personalization:
Blockchain as Security
Using blockchain to prevent any third-party interruption to user data is an ongoing topic in the world of e-commerce. This stems from Blockchain and its capability of allowing users more control over their information. However, that is not to say that they will get less personalized offers or experiences; they will still be able to get the same tailored experience.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Especially after Apple’s premiere of “Vision Pro,” the idea of e-commerce in virtual and augmented reality became concrete. The crucial aspect of these technologies is that they will enable consumers to try on the products before purchasing as if they are already in the store.
Predictive Analysis
With the rapid advancement of technology, especially in the AI segment, predictive analysis will significantly impact the future tendencies of brand strategies.
Sound in E-Commerce
With sound becoming increasingly impactful on technological devices such as smartphones and tablets, e-commerce personalization will also adapt to voice search. This, in turn, will make it easier to provide personalized recommendations for older and disabled people.
Sustainability
With the ongoing crisis of Climate Change, e-commerce platforms will surely incorporate climate-friendly considerations into their personalization strategies to align themselves with the public. The reason for this is the change in the consumer’s demand schematics; more and more people demand sustainable products and services.
What are The Differences Between Personalization and Customization in E-Commerce?
Even though the terms Personalization and Customization are used interchangeably, they account for different services in E-Commerce. The main difference between them is the amount of freedom the consumer has.
- While Personalization offers already personalized recommendations and selections of services and products, customization happens through the specifically chosen options by the consumer.
- While personalization relies heavily on data analyzed by machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence, the consumers shape and select customization.
- Personalization is dynamic and adaptive to the changes in the consumer’s demands. However, once the consumer customizes their products, those settings remain until any changes are made.
- An example of e-commerce personalization is providing product recommendations in search bars based on the browsing and purchase history of the consumer. On the other hand, an example of e-commerce customization is allowing consumers to actively select their clothing, such as skinny fit, baggy, cargo, and many others.
Final Say
E-commerce personalization represents a dynamic and multifaceted approach to online retail, with its effectiveness rooted in its ability to adapt to and anticipate consumer needs. By integrating strategies ranging from basic techniques like personalized emails to advanced AI-driven recommendations, businesses can significantly elevate the online shopping experience.
Personalization fosters customer loyalty and satisfaction and strategically positions businesses in a competitive market. As technology continues to evolve, the future of e-commerce personalization holds promising advancements like blockchain for enhanced security, augmented and virtual reality for immersive experiences, and a greater emphasis on sustainability. Understanding and implementing these personalized strategies is not just beneficial but imperative for businesses aiming to thrive in the ever-changing landscape of e-commerce.